隨著移動互聯(lián)網(wǎng)的發(fā)展,越來越多的應(yīng)用程序需要在多個渠道發(fā)布,以便更好地推廣和獲取用戶。而針對A如何給一個項目打包成apkndroid應(yīng)用程序而言,多渠道打包就是一種非常重要的技術(shù)手段。本文將從原理和詳細介紹兩個方面,對Android多渠道打包進行解析和說明。
一、原理
Android應(yīng)用程序打包后,會生成一個APK文件。這個APK文件包含了所有應(yīng)用程序需要的資源和代碼,還包括了一些特定的標識信息,比如包名、版本號等等。而多渠道打包的核心就在于這個特定的標識信息。在打包時,我們可以通過修改這些標識信息,來實現(xiàn)不同渠道的區(qū)分和識別。
具體來說,Android應(yīng)用程序打包時,會在APK文件的META-INF目錄下生成一個CERT.RSA文件,這個文件包含了應(yīng)用程序的數(shù)字簽名信息。而在這個數(shù)字簽名信息中,包含了一個證書DN(Distinguished Name),這個證書DN就是我們用來區(qū)分不同渠道的標識信息。
舉個例子,我們可以在證書DN中添加一個“channel”字段,來表示當(dāng)前應(yīng)用程序所屬的渠道。比如,我們可以將證書DN設(shè)置為“CN=xxx, OU=xxx, O=xxx, L=xxx, ST=xxx, C=xxx, channel=xxx”,其中,channel字段就是我們用來區(qū)分不同渠道的標識信息。當(dāng)應(yīng)用程序運行時,我們就可以通過讀取這個證書DN中的channel字段,來判斷當(dāng)前應(yīng)用程序所屬的渠道,從而進行不同的處理。
二、詳細介紹
Android多渠道打包的實現(xiàn)方法有很多種,這里我們以Gradle插件為例,來詳細介紹一下具體的實現(xiàn)步驟。
1、添加Gradle插件
首先,我們需要在項目的build.gradle文件中添加Gradle插件的依賴:
“`
buildscript {
repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
classpath ‘com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.1.3’
classpath ‘com.google.gradle:android-gradle-plugin:0.14.0’
}
}
“`
其中,com.google.gradle:android-gradle-plugin:0.14.0就是我們要添加的Gradle插件。
2、配置渠道信息
接著,我們需要在項目的gradle.properties文件中配置渠道信息。比如,我們可以將渠道信息配置為:
“`
CHANNELS=baidu,360,appchina
“`
這里,我們將渠道信息以逗號分隔的形式進行配置。
3、修改APK簽名信息
接下來,我們需要在build.gradle文件中添加一個task,用來修改APK簽名信息。具體代碼如下:
“`
android.applicationVariants.all { variant ->
variant.outputs.all {
outputFileName = “${variant.name}-${defaultConfig.versionName}.apk”
def outputFile = output.outputFile
if (outputFile != null && outputFile.name.endsWith(‘.apk’)) {
def channel
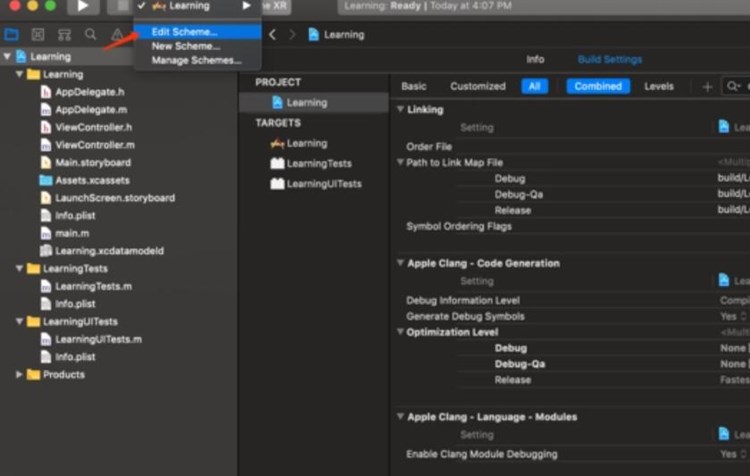
= “channel_” + variant.productFlavors[0].name
zip(outputFile, channel)
}
}
}
def zip(File outputFile, String channel) {
def zipFile = new ZipFile(outputFile)
def tmpFile = new File(outputFile.parent, “tmp-${outputFile.name}”)
def zipOutput = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(tmpFile))
zipFile.entries().each { entry ->
def input = zipFile.getInputStream(entry)
def outputEntry = new ZipEntry(entry.name)
outputEntry.time = entry.time
outputEntry.size = entry.size
outputEntry.crc = entry.crc
zipOutput.putNextEntry(outputEntry)
if (entry.name == “META-INF/CERT.RSA”) {
def certBytes = readFully(input)
def newCertBytes = modifyCert(certBytes, channel)
zipOutput.write(newCertBytes)
} else {
copyStream(input, zipOutput)
}
zipOutput.closeEntry()
}
zipOutput.close()
zipFile.close()
outputFile.delete()
tmpFile.renameTo(outputFile)
}
def readFully(InputStream input) {
ByteArrayOutputStream output = new ByteArrayOutputStream()
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]
int length
while ((length = input.read(buffer)) != -1) {
output.write(buffer, 0, length)
}
output.toByteArray()
}
def modifyCert(byte[] certBytes, String channel) {
def cert = CertificateFactory.getInstance(“X.509”).generateCertificate(new ByteArra蘋果描述文件分發(fā)yInputStream(certBytes))
def tbsCert = cert.tbsCertificate
def subject = tbsCert.subject
def newSubject = new X500Principal(subject.getName() + “, channel=” + channel)
def newTbsCert = new TBSCertificate(
tbsCert.version,
tbsCert.serialNumber,
tbsCert.signature,
new X500Name(newSubject.getEncoded()),
tbsCert.validity,
tbsCert.subjectPublicKeyInfo,
tbsCert.extensions
)
def newCertInfo = new CertificateInfo(
newTbsCert,
cert.sigAlgName,
cert.signature
)
def newCert = new JcaCertStore(Collections.singleton(newCertInfo))
newCert.toASN1Structure().getEncoded()
}
def copyStream(InputStream input, OutputStream output) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]
int length
while ((length = input.read(buffer)) != -1) {
output.write(buffer, 0, length)
}
}
“`
這個task的作用就是遍歷所有的APK文件,然后修改其中的CERT.RSA文件,將其中的證書DN中的channel字段修改為當(dāng)前的渠道信息。具體實現(xiàn)方式是通過ZipFile和ZipOutputStream對APK文件進行讀取和寫入,然后通過CertificateFactory和TBSCertificate對證書DN進行解析和修改,最后將修改后的證書DN重新寫入CERT.RSA文件中。
4、打包并生成多個渠道的APK文件
最后,我們只需要運行g(shù)radle build命令即可,Gradle會自動根據(jù)我們在gradle.properties文件中配置的渠道信息,生成多個渠道的APK文件。
總結(jié):
Android多渠道打包是一種非常重要的技術(shù)手段,可以幫助我們更好地推廣和獲取用戶。本文從原理和詳細介紹兩個方面,對Android多渠道打包進行了解析和說明。通過這篇文章的學(xué)習(xí),相信大家已經(jīng)對Android多渠道打包有了更深入的了解,能夠更好地應(yīng)用到實際開發(fā)中。